Table of Contents
- Introduction to ZTNA
- Why Zero Trust is Crucial
- Critical Steps for Implementing ZTNA
- Case Study: Success in Action
- Conclusion
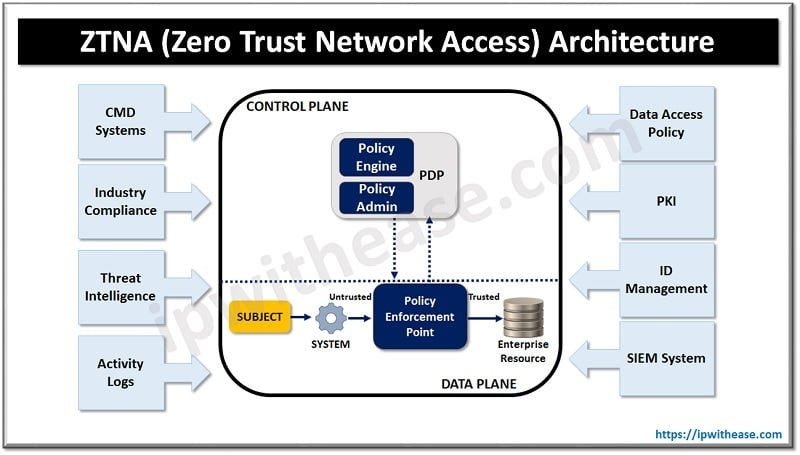
Introduction to ZTNA
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) represents a substantial shift from conventional network security models, providing a more secure and up-to-date approach to connecting users with applications. Effectively incorporating ZTNA providers is crucial for optimizing the security advantages offered by this approach. Traditional VPNs were needed in the past, but they often have broad access privileges and potential vulnerabilities that cyber threats can exploit. On the other hand, ZTNA guarantees a comprehensive authentication process for every access request, granting appropriate access only to authorized users at the proper time.
Why Zero Trust is Crucial
Cyber threats are becoming more complex as digital technology advances quickly. Traditional security models frequently come up short as they concentrate mainly on protecting the network’s perimeter, presuming that individuals within it can be trusted. Nevertheless, this belief is no longer valid with the increase in remote work and cloud-based applications. Zero Trust models reduce these risks by verifying each access request as if it comes from an untrusted network. This technique is particularly crucial because of the increase in telecommuting and the need for access solutions that are both flexible and secure. A zero-trust model can significantly reduce the risks of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Critical Steps for Implementing ZTNA
- Assess Your Current Security Posture: Before implementing ZTNA, it is crucial to thoroughly evaluate your current security framework. This involves identifying gaps and vulnerabilities that cyber threats could exploit. Understanding your security posture will help you determine how ZTNA can address these weaknesses. Documenting your current security measures is crucial in creating a roadmap for a seamless ZTNA implementation. This assessment should include an evaluation of your network architecture, existing security policies, and any tools currently in use for monitoring and managing access requests.
- Choose the Right ZTNA Provider: Choosing the correct ZTNA provider is a crucial choice that can significantly influence the effectiveness of your security tactics. Providers vary in their offerings, so it’s essential to consider factors such as integration capabilities, scalability, and ongoing support. Research various VPN alternatives and read user reviews to find a provider that aligns with your security needs and organizational goals. It’s essential also to seek out providers with solid analytics and reporting tools, as these can give valuable details on user behavior and possible security risks.
- Define and Enforce Access Policies: Stringent access control is a fundamental concept of Zero Trust. It is essential for a successful ZTNA deployment to establish access rules based on user roles and ensure their consistent enforcement. Enforce the principle of least privilege access to limit users to only the necessary resources required for their specific positions. This reduces the chance of unauthorized entry and potential inside dangers. Consistently assess and revise these policies as organizational responsibilities and requirements change. Automated tools for enforcing policies can ensure access policies are consistently implemented throughout the network.
- Monitor and Analyze Traffic Continuously: Continuous monitoring is a crucial practice for identifying potential security threats and ensuring the integrity of your network. By utilizing advanced analytics tools, you can track user behavior and network traffic in real-time, providing valuable insights into unusual or potentially malicious activity. Employing proactive investigation and response measures can help prevent security incidents before they escalate.
- Regular Training and Awareness: Proper user compliance is essential for any security infrastructure, no matter how strong it may be. To uphold a secure environment, it is crucial to offer consistent training to staff on security best practices and the significance of Zero Trust principles. This training should cover topics such as recognizing phishing attempts, creating strong passwords, and following secure data handling procedures. Promoting a focus on security awareness in the company can significantly decrease the possibility of human errors undermining your security initiatives.
Case Study: Success in Action
Consider a mid-sized enterprise that implemented ZTNA after experiencing a severe security breach. Initially, the company’s traditional security measures were insufficient in preventing unauthorized access, leading to a significant data loss incident. By adopting Zero Trust principles, the company restructured its access policies, implemented MFA, and began continuous monitoring of network traffic. As a result, they significantly reduced unauthorized access incidents and improved their overall security posture. This real-world example demonstrates the efficacy of ZTNA in mitigating security risks and protecting valuable digital assets.
Conclusion
Shifting towards a Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) model is not just a temporary fad but an essential requirement in today’s quickly changing security environment. With the rise of remote work, organizations face unique challenges that demand a heightened focus on network security. The proliferation of intricate cyber threats and the dynamic nature of digital environments underscores the urgency of adopting ZTNA principles. This model stresses that all users and devices should not be automatically trusted, whether inside or outside the network boundary. Companies can enhance their defenses against advanced attacks by utilizing thorough verification procedures and strict access controls.
Organizations must adhere to several key strategies to optimize security measures and safeguard online resources. These include adopting a least privilege access approach, where users receive only the permissions necessary for their specific roles, thereby minimizing potential exposure to threats. Additionally, continuous monitoring and real-time analytics can help identify and respond promptly to unusual activities, further strengthening the security framework. ZTNA’s emphasis on micro-segmentation allows organizations to isolate sensitive data and applications, making it significantly more challenging for attackers to traverse the network if a breach occurs.
Through meticulous verification and strict access control, Zero Trust emerges as a powerful solution to organizations’ modern security challenges. It fortifies defenses against current cyber threats and creates a resilient infrastructure capable of adapting to future vulnerabilities. In an era where cyber threats are more pervasive and sophisticated than ever, embracing a zero-trust approach is essential for any organization committed to protecting its digital assets and ensuring the integrity of its operations.